By default the most commonly used ssh port is the port 22. Due the fact that its the most common port it can become a security vulnerability for your system or server(s). Thus, it is always important to change the ssh port to further increase the security of your machine and/or server.
This guide will be showing you how you can easily change the ssh port in Linux to a different one of your preference.
Modifying the Firewall
It is important that you do not skip this step as you need to adjust your firewall to accept connections to the new port you’ll be changing it to. If you forget to do so you will not be able to ssh back in into your machine or server through the default port 22 or even the new one you changed it to.
Debian and Ubuntu users can use ufw to allow the new port:
ufw allow new_port/tcp
ufw allow 1201/tcpOn the other hand, RHEL-based distros such as CentOS use FirewallD:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=NEW_PORT/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadAlso, we need to modify the SELinux rules in RHEL-based distros:
sudo semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp NEW_PORTHow to Change the SSH Port in Linux
It is important to note that if you use the OpenSSH Server, regardless of the distribution you are using, whether its Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, Fedora, etc. the process to change the default ssh port it will be exactly the same.
To start, we need to edit the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file. In our case we will be using the nano editor, but, feel free to use an alternative such as vi or vim, whichever you are most comfortable with.
nano /etc/ssh/sshd_configThen, find the line that states: #Port 22, uncomment it and change the 22 to the port you’d like to change it to. In our case we’ll be changing it to 1201
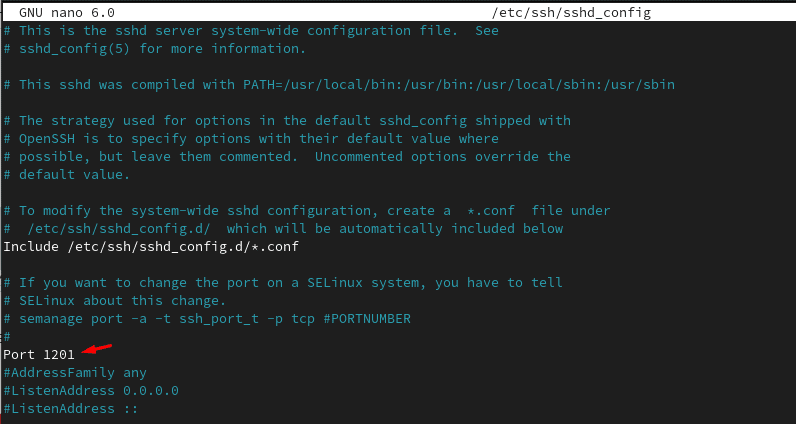
Then save by hitting CTRL+ X. Then we need to restart the SSH service:
sudo systemctl restart sshd #Fedora / CentOS
sudo systemctl restart ssh #Debian / UbuntuIn order to verify everything is working as intended we can use the ss command to verify:
ss -an | grep NEW_PORT[root@linuxify ~]# ss -an | grep 1201
tcp LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:1201 0.0.0.0:*
tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::]:1201 [::]:*
From there we can see that our machine is already listening in port 1201.
Summary
This guide showed you how to change the ssh port and verify that it has been successfully changed and ready to go.